This post may contain affiliate links which means I will get a commission if you make a purchase at no additional cost to you. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. Please read my disclosure for details.
While most Americans trust their food supply is safe, a startling reality lurks in grocery store aisles: numerous food additives banned in other countries remain perfectly legal in the United States. From bread improvers linked to cancer to synthetic dyes associated with behavioral changes, these controversial ingredients continue appearing in everyday American products.
The FDA’s approach to food safety often diverges from international standards, creating a complex landscape where substances prohibited across Europe, Asia, and beyond freely circulate in U.S. food products. This regulatory gap raises important questions about American food safety standards and consumer awareness.
Brominated Vegetable Oil (BVO)

WANT TO SAVE THIS RECIPE?
Brominated vegetable oil (BVO) serves as an emulsifier in citrus-flavored soft drinks and sports drinks across the United States.
While legal in America, this substance faces bans in Japan, the European Union, and the UK due to serious health concerns. The FDA proposed a ban in November 2023 after studies showed BVO can build up in body fat, potentially causing memory loss and nerve problems.
Medical reports link BVO to neurological symptoms including tremors, fatigue, and headaches. The additive may also affect thyroid function by competing with iodine uptake, while research indicates connections to reproductive damage and behavioral changes.
Related Post: XXXX
Potassium Bromate

Potassium bromate functions as a dough improver in bread products throughout the United States, creating texture that many consumers prefer. Despite its continued use in American bakeries, this chemical faces outright bans in Europe, China, and India.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer identifies it as a possible human carcinogen, backed by studies showing cancer development in laboratory animals. While the FDA maintains that proper baking converts it to a harmless substance, international health authorities remain unconvinced of its safety for food production.
Related Post: XXXX
Propylparaben

Propylparaben functions as a preservative across multiple industries, appearing in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and processed food products in the United States. California recently prohibited this chemical under the California Food Safety Act, citing substantial health risks.
Scientific studies point to propylparaben’s ability to interfere with the body’s endocrine system. The compound can copy estrogen’s effects in the body, leading to hormone disruption. Research indicates links between propylparaben exposure and both developmental issues and reproductive system problems, prompting health agencies worldwide to question its continued use in food products.
Related Post: XXXX
Red Dye No. 3

Red Dye No. 3 remains legal in U.S. food products, appearing in candies, baked goods, and snack items despite mounting safety concerns. The FDA banned this synthetic coloring from cosmetics, yet allows its continued use in food manufacturing.
Animal studies demonstrate clear links between Red Dye No. 3 and thyroid tumor development. Medical researchers report associations with behavioral changes in children, particularly increased hyperactivity.
California took action in 2023, becoming the first state to prohibit Red Dye No. 3 in food products through the Final Report on Safety, marking a shift in U.S. regulatory approaches to this controversial additive.
Related Post: XXXX
Titanium Dioxide

Titanium dioxide appears in American candies and processed foods as a white coloring agent, though the European Union has blocked its use. The substance, while permitted in U.S. food products, carries health risks that prompted international restrictions.
Research indicates titanium dioxide particles may irritate the digestive system and lead to inflammation of the gut wall. Scientists found the substance can accumulate in digestive tissue, raising concerns about long-term intestinal health effects.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer labels titanium dioxide as potentially cancer-causing when inhaled, though studies continue on its effects when consumed in food products.
Sign up now to receive our exclusive e-cookbook filled with top-rated recipes for FREE!
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA)

BHA, a common preservative in U.S. food products, appears in snack foods, breakfast cereals, butter, meats, and frozen items. The International Agency for Research on Cancer identifies BHA as a Final Report on Safety, making it a subject of ongoing food safety debates.
Studies point to BHA’s connection to both cancer development and hormone system interference. While the FDA continues to allow BHA in American food products, international health organizations question its safety.
The preservative remains particularly concerning due to its presence in everyday items like cake mixes and processed meats, leading several countries to restrict its use in food manufacturing.
Related Post: XXXX
Artificial Food Dyes (Yellow No. 5, Yellow No. 6, Blue No. 1, Blue No. 2)

Common artificial food dyes, found extensively in American candies, sodas, and snack products, remain under scrutiny for Final Report on Safety. These synthetic colors, while approved by the FDA, face mounting evidence linking them to adverse health effects.
Medical studies show these dyes may trigger allergic reactions and behavioral changes, particularly in children. Reports document increased hyperactivity in sensitive individuals after consuming products containing these synthetic colors.
Several U.S. states now consider legislation to restrict these additives, following international precedents where many artificial dyes face strict regulations or outright bans.
Related Post: XXXX
Azodicarbonamide

Azodicarbonamide, a white powder used in U.S. bread manufacturing, acts as both a flour bleaching agent and dough conditioner. The FDA permits this chemical in American food production despite international restrictions on its use. Medical research identifies azodicarbonamide as a respiratory sensitizer, with studies showing links to asthma among food industry workers.
When heated during baking, the substance breaks down into compounds that Final Report on Safety Assessment has linked to cancer development. Several American states now consider following international examples by restricting this additive, as evidence mounts regarding its potential health risks to consumers and manufacturing workers.
Related Post: XXXX
Recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone (rBGH)
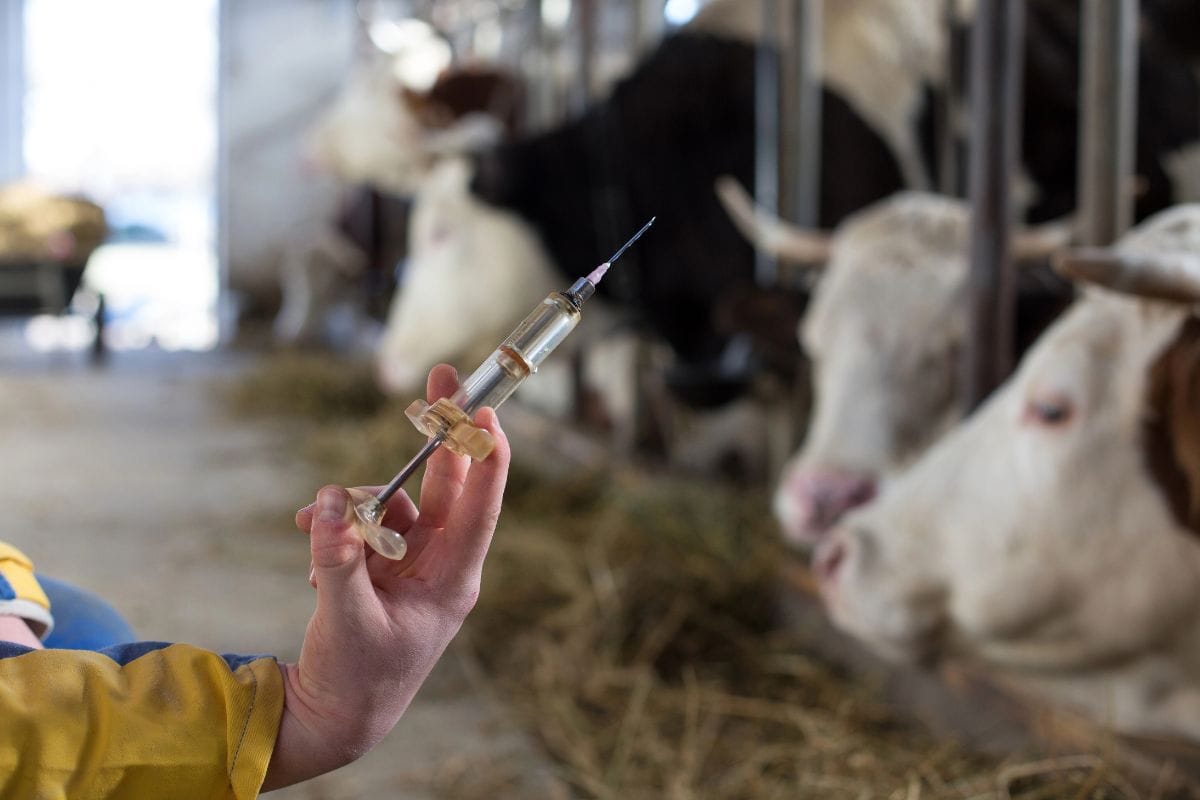
Recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone, a synthetic version of a natural cow hormone, gets injected into dairy cows to boost milk output in U.S. dairy farms. While permitted in American dairy production, many countries have stopped its use, citing animal health risks.
Studies show rBGH increases insulin-like growth factor one (IGF-1) in milk from treated cows. The higher IGF-1 levels concern Final Report on Safety officials, as research points to possible connections between elevated IGF-1 consumption and cancer development in humans.
Several international markets reject milk products from rBGH-treated cows, reflecting widespread safety apprehension outside the United States.
Related Post: XXXX
Olestra/Olean

Olestra, marketed under the brand name Olean, appears in American snack foods as a fat substitute aimed at reducing calorie content. The FDA permits this synthetic fat replacement despite documented health complications in consumers.
Medical reports show Olestra blocks the body’s absorption of essential vitamins. Consumer studies document widespread digestive problems among people who eat Olestra-containing products.
The most notable side effects include severe gastrointestinal distress and anal leakage, prompting Final Report on Safety warnings on product labels. While manufacturers continue using this additive in U.S. snack foods, many countries refuse to allow Olestra in their food supply.
Sign up now to receive our exclusive e-cookbook filled with top-rated recipes for FREE!
The Growing Gap Between U.S. and Global Food Safety Standards

The continued presence of these ten controversial ingredients in the American food supply highlights a significant divergence between U.S. and international food safety standards.
While the FDA maintains these additives are safe at approved levels, mounting scientific evidence and international regulatory actions suggest otherwise.
As more states like California take independent action to restrict these substances, pressure builds for federal regulators to reassess their positions.
The growing awareness of these ingredients’ potential health risks may eventually force a broader reconsideration of U.S. food safety policies, bringing them more in line with international standards.
Sources
- Consumer Reports: 5 Dangerous Ingredients That Are in Our Food But Shouldn’t Be
- Healor: What’s Brominated Vegetable Oil and Why Should You Care
- The Acheson Group: 28 Food Ingredients/Additives That May Be Banned Across the Country
- National Agricultural Law Center: Update on Proposed Food Additive Bans
- Psychiatrist.com: FDA Moves to Ban BVO Amid Neurological And Other Health Concerns
- GoodRx: 5 American Food Ingredients That Are Banned Abroad
- CBS News: U.S. food additives banned in Europe: Expert says what Americans eat is making them sick
- Environmental Working Group: FDA finds brominated vegetable oil no longer safe for use in food
- GoCoCo: 13% of food products at risk of being banned in US States
Disclaimer: This list is solely the author’s opinion based on research and publicly available information.
8 Everyday Foods Facing Higher Prices Under Trump’s Tariffs

President Trump’s recent tariffs on imports from Mexico, Canada, and China have significantly impacted the prices of many everyday grocery products. With a 25% tariff on Mexican and Canadian imports and a 20% tariff on Chinese goods, many household staples are becoming more expensive.
Read it here: 8 Everyday Foods Facing Higher Prices Under Trump’s Tariffs
13 Worst Grocery Store Tricks Designed to Mislead Store Shoppers

Ever walked into a grocery store for just a few essentials, only to leave with a cart full of things you didn’t plan to buy? It’s not your lack of willpower—it’s by design!
Read it here: 13 Worst Grocery Store Tricks Designed to Mislead Store Shoppers
10 Old-School Restaurant Chains That Barely Exist Now

America has seen its fair share of beloved restaurant chains come and go. While some nostalgic favorites have completely disappeared, others are hanging on by a thread, with only a handful of locations left. These restaurants once thrived, serving up classic American comfort food, burgers, and shakes to generations of diners.
Read it here: 10 Old-School Restaurant Chains That Barely Exist Now
Is Walmart+ Still Worth It in 2025? The Truth After 3 Years

Could you be missing out on major savings and life-changing convenience? After three years with Walmart+, I’m sharing the honest truth about what’s worth it—and what’s not. Don’t sign up (or skip out!) without reading this first!
Read it here: Is Walmart+ Worth It? Honest Review 3 Years Later!
You’ll love these related posts:
